The State Voter Suppression Law
Introduction
Background of the Study
The state voter suppression law is one of the nominal U.S. historical frameworks enhancing discrimination across dynamic races. Since the end of the Reconstruction period (1865-1877), researchers have noted a significant increase in voter suppression influence (Barreto et al., 2019). During the Reconstruction period, African Americans in the former confederacy attained the rights to run for political positions at the federal, state, and local levels, and serve as members of the jury and the voting rights. Equality advocacy was mainly facilitated by the 14th and 15th amendments in the American constitution that guaranteed all U.S. citizens the voting right, especially among African Americans, while criminalizing terror ideologies from white supremacists. However, after the Reconstruction era, African Americans holding political positions mainly in the South encountered threats, intimidation, and killings. Southern state governments amended regulations restricting the participation among African Americans.
Statement of the Problem
The incorporation of voter suppression law is a prominent issue that violates the essence of constitutional human rights on equality. According to the research, racial discrimination is a common sociological issue in American society (DuBose, 2021). The main belief encompasses the distinction between white supremacists and minority ethnic groups. Therefore, the government’s mandate is to establish standard practices that promote uniformity and the effective distribution of benefits and opportunities among the citizens despite ethnic identity.
Purpose of the Study
This study seeks to assess the state voter suppression laws and their impact on the African American ethnic group in the U.S. Evaluating the impact of state voter suppression laws fosters the understanding of effective strategies to alleviate discrimination.
Research Questions
- What is the impact of state voter suppression law on U.S. citizens?
- What is the relationship between social justice and voter suppression law?
Definition of Terms
- Vote
- It is an opportunity to express a wish to follow a particular action plan.
- Voter suppression -It is a strategy used to influence election outcomes by marginalizing certain groups or individuals.
- It is an opportunity to express a wish to follow a particular action plan.
- Law
- It is the system of rules within a nation.
- Racial discrimination -It is the denial of rights based on ethnic identity
- It is the system of rules within a nation.
Literature Review
Introduction
This study encompasses an evaluation of the historical background of state voter suppression law and its implication for American society. The onset of state suppression law negatively affected African Americans mainly because of the denial of voting right for equal representation in the government. It is the responsibility of relevant stakeholders to uphold the constitutional framework of democracy to enhance equality despite disparate ethnic groups.
State Voter Suppression Law
State voter suppression law is a multidimensional phenomenon that enshrines the outcome of racial discrimination in political practice. According to research by Baretto et al. (2019), the development of the Reconstruction era enhanced social equity through the constitutional policies. However, the challenge involved the discordance from the southern states regarding voting rights among African Americans. The main aim of the protest encompassed promoting the whites’ dominance in the state government with minimal influence from the federal institutions. Despite the efforts from the Northern state administrations, the southern states managed to influence the change in the policies and foster state voter suppression laws.
Racial discrimination is a sociocultural, economic, and political issue that affects the enforcement of laws and regulations. Hardeman et al. (2022) investigated the implication of whites’ dominance in the political parties and noticed that the key purpose enshrined suppressing African American freedom and rights. One of the vital initiatives involved the accordance of voting rights. During Reconstruction, African Americans voted a significant percentage of the African American leaders in political seats. The aspect overwhelmed the whites’ influence in the political domain. As a result, the southern states resolved to violence, intimidation, and change in constitutional voting regulations to promote intensified whites’ dominance in the political platform.
Different approaches were exploited to ensure the disenfranchisement of African Americans from voting. According to Epperly et al. (2020), white supremacists used intimidation, literacy, comprehension tests, poll taxes, violence, historical background, good character evaluation, and fraudulent activities to enforce state voter suppression law. The study by Epperly et al. (2020) further indicates that racial discrimination emanated from the period before the American civilization when African Americans were mainly slaves in the plantation farms owned by the whites. Abramovitz et al. (2019) indicate that excellent legal clauses that contributed to the alleviation of voter suppression law enshrine 24th amendment in 1964, Civil Rights Act in 1964, and the Voting Rights Act in 1965 of the U.S. constitution. Primarily, the constitutional amendment was steered through by the accountability among the state governments to report the prominence of the change of the constitutional voting rights to the federal court.
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 was signed by president Lyndon Johnson fostering the alleviation of racial discrimination in voting practices. DuBose (2021) assessed the significance of voter suppression as either an American legacy or a modern factor. Based on American history, DuBose (2021) stipulated that enhancing the outlaw of discriminatory voting practices featured dynamic aspects. The legal clause established the illegalization of literacy tests and the necessity to assess good character based on the ethnic background as a prerequisite during voting. In this case, Ross (2019) supports that African Americans, therefore, attained optimal security and support system from the implementation of the Voting Rights Act of 1965, thus intensifying the active campaign mobilization. Further, the clause empowered the U.S attorney general to investigate the legitimacy of poll taxes during elections. In a different spectrum, the African Americans benefited from the condition that the federal government is mandated to oversee the voter registration process, especially in areas with lower participation in the voting process among the non-whites.
Role of the Constitution
One of the steering principles in American governance is the advocacy for democracy. In this case, Romero (2020) establishes that it is the responsibility of key stakeholders to ensure equality across dynamic ethnic groups. Therefore, the researcher argues that the incorporation of the constitution offers a standard platform utilized to reference conditional behavior and perspective on particular issues. The key role of the constitution involves articulating the limitations and the rights of institutions and individuals. Despite the ability to use the constitution as a tool to promote social justice, after the reconstruction era, the White Americans from the Southern states prominently exploited the constitution to segregate African Americans.
Apart from enforcing social justice, the constitution significantly contributes in the provision of institutions fostering order across society. Raven (2018) depicts that although the white supremacists manipulated the system, the essence of democracy further reconstructed the mainframe of preventing discriminatory practices, especially towards African Americans. Therefore, the constitution prominently empowered the federal government to enhance equality based on the roles and influence to state administration. It is the responsibility of relevant entities established through the constitutional clauses to promote equity.
Impact of State Voter Suppression Law on Social Justice
The voter suppression law significantly contributed to the segregation of African Americans in the country’s sociocultural, economic, and political development. Norris (2019) argues that social justice entails the advocacy for equal rights among their counterparts. In this case, Norris (2019) justifies that it is important to establish conditional insights that impact interdependence among people despite ethnic identities. Discrimination hinders democratic practice thus the prominence to ensure distributive accountability across leadership mainframes.
Social justice is an essential factor due to the facilitation of optimal engagement among all citizens. Hing (2018) assesses the impact of voter suppression law and realizes that the approach fostered the discriminated participation of the whites-only in the political influence while intimidating African Americans. Therefore, the regions experienced frequent violence and tension among individuals based on ethnic diversity and identity. Ideally, the sociological environment proved unsuitable for the American citizens while the government faced optimal hurdles in playing the role of protecting the citizens.
Summary
The voter suppression law is an initiative that threatens American democracy mainly because of the corruption of the political leadership essence. In this case, the researchers establish that it is the responsibility of the state and federal government to ensure social justice among the citizens. The main role of the constitution is to facilitate order and a distributive justice system across distinct platforms. Therefore, the implementation of the voter suppression law was a profound violation of the constitutional role to ensure the protection of the citizens and advocacy for equality.
Methodology
Introduction
The study was exploratory research into the impact of voter suppression laws to the American citizens mainly because of ethnic diversity. The researcher used questionnaires as the primary data collection tools and further utilized a mixed-method analysis approach. In this case, the study focused on the collection of data based on the research questions and compared it to the previous literature to derive inductive and deductive conclusions.
Data Gathering
The data collection tool encompassed the questionnaire that comprised open and closed-ended queries based on the topical issue. The researcher used stratified random sampling in the distribution of the questionnaires across the Northern and Southern states to alleviate biasness. The sample size encompassed 100 participants constituting government officials and community members. The data collected were tabulated, analyzed, and presented using charts and graphical illustrations.
Findings
The researcher distributed the questionnaires among 100 participants regarding the topical issue. The questions encompassed:
- What is the impact of state voter suppression law to U.S. citizens?
- What is the relationship between social justice and voter suppression law?
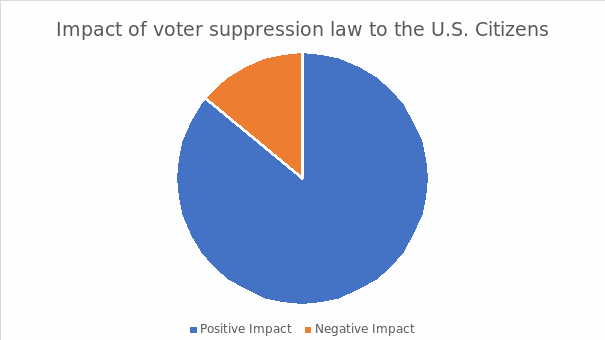
The first question rendered a dynamic response among the participants mainly because of the profound American history. According to figure 1.0, at least 86% of the respondents established that the voter suppression law contributed to the realization of prominent racial discrimination practices across the nation. 14% of the respondents argued that the initiative fostered the apt influence of white supremacism and intimidation among African Americans despite the advocacy for democracy through the constitutional laws.
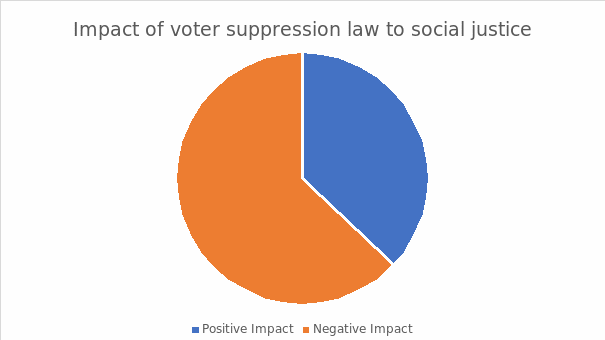
The second question attributed to the attainment of a profound insight concerning the interpretation of social justice. Although the majority of the respondents interpreted social justice as democracy, at least 63% agreed the voter suppression law violated the system’s goal. According to figure 2.0, 37% of the respondents established that the voter suppression law incidence contributed to the promotion of social justice mainly because of raising the flag regarding the imminent discriminatory practice.
Conclusion
State voter suppression law significantly contributes to racial discrimination and the lack of coherence among Americans mainly because of the prominence on racial identity and social status. Equality is a necessity in the U.S. mainly because it attributes to the balanced notion on the distribution of accrued benefits among all citizens. The incorporation of the Civil Rights Act and Voting Rights Act significantly enhanced African Americans’ ability to exercise their mandate to participate in elections.
It is recommended that further studies focus on the exploration of racial discriminatory practices and their effect to economic growth and development to understand the profound necessity of apt community inclusivity in national unity. In this case, it is also recommended that the additional literature renders insights among American leaders concerning emerging trends and the necessity to promote social equity through the policies.
The key limitation encountered during the study encompassed focus on the influence of voter suppression law on U.S. citizens, mainly African Americans. However, the delimitation encompasses the provision of inductive insights to enhance an in-depth exploration of the role of politics in racial discrimination. Another challenge involved limited time to adeptly collect data and analyse it. Therefore, the researcher integrated primary results with previous literature contexts to derive significant insights on a topical issue.
References
Abramovitz, M., Sherraden, M., Hill, K., Smith, T. R., Lewis, B., & Mizrahi, T. (2019). Voting is social work: Voices from the national social work voter mobilization campaign. Journal of Social Work Education, 55(4), 626-644.
Barreto, M. A., Nuño, S., Sanchez, G. R., & Walker, H. L. (2019). The racial implications of voter identification laws in America. American Politics Research, 47(2), 238-249.
DuBose, R. (2021). Voter suppression: A recent phenomenon or an American legacy?. The University of Baltimore Law Review, 50(2), 2.
Epperly, B., Witko, C., Strickler, R., & White, P. (2020). Rule by violence, rule by law: Lynching, Jim Crow, and the continuing evolution of voter suppression in the US. Perspectives on Politics, 18(3), 756-769.
Hardeman, R. R., Homan, P. A., Chantarat, T., Davis, B. A., & Brown, T. H. (2022). Improving the measurement of structural racism to achieve antiracist health policy: Study examines the measurement of structural racism to achieve antiracist health policy. Health Affairs, 41(2), 179-186.
Hing, A. K. (2018). The right to vote, the right to health: Voter suppression as a determinant of racial health disparities. Journal of Health Disparities Research and Practice, 12(6), 5.
Norris, P. (2019). Do perceptions of electoral malpractice undermine democratic satisfaction? The US in comparative perspective. International Political Science Review, 40(1), 5-22.
Ravel, A. (2018). A new kind of voter suppression in modern elections. U. Mem. L. Rev., 49, 1019.
Romero, M. (2020). Sociology engaged in social justice. American Sociological Review, 85(1), 1-30.
Ross, B. L. (2019). Passive voter suppression: Campaign mobilization and the effective disfranchisement of the poor. Nw. UL Rev., 114, 633.
Appendix
Questionnaire
This study encompasses the evaluation of the impact of voter suppression law to U.S citizens and the social justice system. The researcher aims to collect primary data affirming the significance of equity and coordination among relevant stakeholders. Kindly fill in the responses accurately. Confidentiality will be highly maintained.
- Respondent’s signature…………………… Date……………….
- Interviewer’s signature
- Date
Section A: Social Economic Details (Kindly fill in the spaces and boxes provided)
- A1 Place of residence
- A2 Age:
- 0-19 [ ]
- 36-59 [ ]
- 20-35 [ ]
- 60 and above [ ]
- A3 Occupation
- Businessman [ ] d) Farmer [ ]
- Student [ ] e) Self-employed [ ]
- Not employed [ ] f) Civil servant [ ]
- A4 Highest level of education attained
- University level [ ] c) Secondary level [ ]
- College level [ ] d) Primary level [ ]
- A5 Gender:
- Male ( )
- Female ( )
- A6 Range of Income (Kshs)
- 1-50,000 [ ]
- 100,001-250,000 [ ]
- 50,001-100,000 [ ]
- 250,001 and above [ ]
- A7 Range of Expenditure (Kshs)
- 1-5000 [ ]
- 25,001-50000 [ ]
- 5001-25000 [ ]
- 50000 and above [ ]
Section B: Did voter suppression law significantly impact the U.S citizens?
- Yes ( )
- No ( )
- Kindly give a reason(s) for your answer.
Section C: Did the voter suppression law impact the social justice system?
- Yes ( )
- No ( )
- Kindly give a reason(s) for your answer.

