Legal Framework of Value-Added Tax in the UAE
Introduction
In order for the concept of tax morality to be determined, it is essential to identify the legal framework for the flat tax that consumers pay once they purchase an item. Since this type of taxation is implied with every purchase, consumers cannot avoid it. Hence, the morality aspect becomes less significant for the customers. The monetary addition is the Value Added Tax (VAT), and it is present during the majority of transactions between a customer and an actor providing a service or selling a good. The Value Added Tax was issued in 2017 in the Federal Decree-Law No. (8). As a result, the rate of 5% added to the cost of goods and services can then be used by the government to improve the public sector.
VAT does not correlate with a presence on every step of the supply chain. Instead, the taxation is levitated on the consumer in the final stage of the transaction. The legal implementation that has created an environment in which service providers were reluctant is the fact that their new roles implied becoming agents in the tax collection process . Creating a legislative initiative was facilitated by multiple organizations, and multiple GCC states have joined the legal agreement to integrate a VAT system in 2016. As a result, UAE was one of the countries that followed through with the agreement relatively quickly and successfully. As a result, the system in which the state is able to access funds from transactions is not only beneficial in terms of a reduction of the oil industry on the financial potency of the country but also creates a basis for improved public services, infrastructure, and other essentials.
The legal framework regarding tax morality is tied to the country’s aim to minimize illegal activity and maximize lawfully and legitimized transactions backed up through legislative power. An outcome of low tax morality is tax evasion, which is an illegal act that is the result of improper taxation. Moreover, the legal punishment but such activities may not exceed a penalty constituting five times the amount of money that was deliberately withheld and would, otherwise, be added to the country’s funds. While legal repercussions regarding this subject are rare, the legislative basis for punishing low tax morality exists. This facilitates regulatory implications that create an environment in which tax morality can be addressed on a state level. However, tax morality cannot be fully addressed through legal frameworks since the subject implies multiple different factors affecting the outcomes. Moreover, since the Federal Decree-Law No. (8) has been integrated into the legislative system relatively recently, the level of tax morality is impacted by the population’s lack of experience and apprehension towards changing the standard business practices.
As a result, although the legal framework addressing tax morality exists, it may be less effective due to the nuanced approach which has been recently applied and the overall environment in which business owners have to take the role of government agents and collect the tax. Instead, a reasonable consideration would be looking at the complex process and mindset when it comes to an understanding of the purpose of applying VAT, the benefits correlating with such strategies, and the negative implications linked to illegal evasion of taxes. In this case, the legal framework becomes one of the many aspects which ultimately form societal tax morality and an agreement of consumers and business owners to only engage in ethical and lawful practices.
Value-added tax is regarded as a consumption tax imposed on products and services at the time of value addition at the supply chain stage. In order to enforce tax morality, the governments in the UAE have created effective laws, and the citizens of the country are required to follow these laws. There are two kinds of taxes imposed in the UAE, which are value-added tax and excise tax. The government of the UAE needs to create some new rules to earn taxable money for developing the country. This thesis will discuss value-added tax and the impact of tax morality on everyday people in the UAE.
Aim of the Research
This research aims to analyze the impact of value-added tax and its effect on tax law compliance in the UAE.
The Objective of the Research
- To understand the importance of tax morality
- To know the impact of value-added tax collection in the UAE economy
- To compare value-added tax compliance in the UAE throughout the years 2018 to 2021 using the number of registrants
- To give recommendations for improving the aspect of value-added tax morality in the UAE
Research Question
- How can UAE improve Tax regularity framework?
- What is the importance of tax morality?
- What is the impact of value-added tax collection in the UAE economy?
- What are the recommendations for improving the aspect of value-added tax morality in the UAE?
Research Problem
In January 2018, the government of the UAE had introduced a new tax called Value-added Tax (VAT). This tax is charged on a wide range of products and services, such as hotels and restaurant services. The government of the UAE introduced VAT to increase its revenue amount for the development of the country. The research problem focuses on the lower collection of value-added tax because of poor tax mortality among the population of the UAE.
Literature Review
Conceptual framework
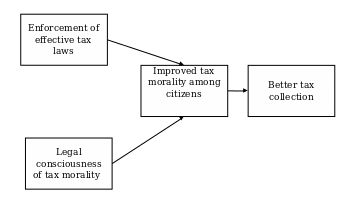
Tax Morality
Tax morality is an ethical activity that shows whether people pay taxes according to the tax rate and applicable laws. Tax morality is essential in collecting taxes, as many tax systems rely on the willingness of taxpayers to comply with laws and regulations to pay the tax dues for majority of the revenue collection process. Studies show that several factors affect tax morality, such as age, education, and gender. For example, women have higher tax morality than men which lead to better compliance. The UAE government has introduced Value-added Tax at the rate of 5%, aiming to diversify the sources of income and move towards non-oil revenues in order to be able to provide the citizens with better healthcare service, welfare, and defense. Based on a survey conducted, the citizens of the UAE are disappointed After introducing this new tax rate because they now have to pay more money to buy new products and services, which will reduce their savings. On the other hand, since January 2018, tax revenue has increased, and the government has now developed more projects in the UAE. For the government to improve tax morality, it needs to spread more awareness and educate the citizens on the importance of paying taxes. in addition, creating fair and transparent value-added tax laws that all citizens will understand adequately will help in easing the process of tax collection.
Measures to Check the Impact of Tax Morality
After creating a new tax, the government of the UAE will need to check and analyze the workability of these laws in the country. According to Miller, creating a new tax method can change the lifestyles of the citizens and the value-added tax policies in a country. For that reason, the government of the UAE needs to check the aspect of tax collection properly after charging tax on the market.
Sociology
There is need to analyze the financial position of their citizens. If the tax rate is very high, then it can influence the market policy. In the market, value-added tax can increase the product’s price, leading to customers not being able to buy essential products. For that reason, after charging 5% VAT on products, the government of the UAE needs to analyze the market policies. After applying the law, if the local market grows its business successfully, it will be claimed as affordable tax law. If the local markets do not grow successfully, this new law will be considered a non-affordable law. Then the government will need to rectify the law and try to make it transparent and affordable. In addition to analyzing the tax rate’s affordability, raising awareness plays a vital role in tax collection. For instance, tax authorities must consider continuing education programs and effective monitoring mechanisms to determine that taxpayers have a good and adequate knowledge and understanding of tax subjects through awareness campaigns, leaflets and brochures, and interactive websites.
For this reason, sociology is a crucial flaw in understanding the impact of new tax laws and tax rates. The government of the UAE will need to spread more social awareness to emphasize the importance of paying value-added tax properly. If the citizens of the UAE understand VAT law properly, then they can grow their interest in contributing to VAT collection.
Culture
There needs to be a positive culture in the UAE that helps in the collection of tax effectively. Better tax morality in society is expected. The citizens of the UAE need to understand the importance of paying taxes.
Taxable products
According to Verma et al., the UAE government has applied VAT on 100 food items, cars, cycles, electronic products, jewelry, smartphones.
Impacts on business in UAE
After applying VAT, product prices in the UAE market have increased. For that reason, business owners need to control their production costs to make the items affordable for all customers. In order to maintain the price, owners of the companies are required to reduce their production price without compromising the quality of products which can impact the cash flow statement of these companies. After applying this tax, the CEO of the companies cannot predict the future risks correctly because the tax rate of VAT can increase in the future.
Advantages of VAT in UAE market
After applying Value Added Tax, the government has earned more revenue than in the previous years. For that reason, they can improve more infrastructures in the UAE with this revenue amount. Now, they can invite some foreign companies to invest money in the UAE. The companies accepted this tax and changed their policies and strategies to add this tax to their financial statement. It is a historical movement for all businesses in the UAE.
Understand the limitations of this law
Federal Decree-Law No. (8) of 2017 is the primary value-added tax law in the UAE. The government of the UAE will need to understand the limitation of the law after applying it in the market. According to Yaghi & Alibeli, a change in the law can change market policies. Therefore, the UAE government will need to identify the limitations of this law and try to address the solutions.
Statistics of Taxation in UAE
Tax rate
According to the Ministry of Finance report, the rate of value-added tax of the UAE is 5%. According to Yaghi & Alibeli, this tax is charged on products or services such as five-star hotels and restaurants, cosmetic products, electronics products, food items, social services, education, and cars. While buying products, the citizens of the UAE need to pay 5% VAT on the amounts of products. Additionally, the value-added tax is charged on products, health, and education services. That means the customer must pay VAT while they buy their products and services. After increasing the amount of tax raised, the government of the UAE can use the amount to develop the country more than the previous year. For that reason, the government of the UAE needs to be concerned about collecting the value-added tax properly. They can create some new laws for earning tax properly. The citizens of the UAE need to understand the importance of value-added tax. If they are correctly paying the tax, then the UAE can develop more than the previous year.
For that reason, the price of products in the UAE has increased since 2018. However, the government has earned more revenue than in previous years. After applying taxes, the citizens of the UAE have faced pricing issues. Nevertheless, they have accepted this finally, and they are growing their interest in this new law. The government of the UAE needs to be concerned about the activities of the market and needs to analyze that everyone is paying taxes.
Comparison between the Countries
The tax rate of the UAE is much more affordable as compared to some other countries. In this result, it is shown that Arab’s value-added tax rate is more affordable compared to Africa, America and Germany. The value-added tax rate is also dependent on the currency value in a country. For America and Germany, their currency value is higher as compared to the UAE. For this reason, the value-added tax rate is higher as compared to the UAE. However, the government of the UAE needs to make this tax rate more affordable to be paid by customers. On the other hand, they can separate this tax rate depending on the product’s price. in the UAE the laws are not effective for the collection of the tax. For that reason, many businesspersons avoid paying value-added tax though the customers paid their tax with the amount of product. Therefore, the government of the UAE needs to create some laws to collect tax from the people and businesspersons.
Research Methodology
The research will be using both primary and secondary data collection. Information on tax morality will be collected from public government reports based on the amounts collected per year. The survey will be conducted among citizens about their participation in tax filing. The interview will be conducted with the officials from Federal Tax Authority in the UAE. The research will include qualitative in-depth interviews on the officials’ perspectives of the motivation for tax evasion among businesses in the UAE. Later, the interviews will be analyzed by the coders who would identify some of the most common themes and phenomena mentioned during the conversation.
History of Tax Morality Theory
Tax morality theories are inextricably linked to issues of public services and commodities provision. Due to the presence of countless usually anonymously operating entities, the taxation issue differs from conventional public good providing circumstances. In case public supervision is expensive, determining appropriate audit rates and punishment systems becomes a significant challenge. Therefore, tax morale theory is based on the innate incentive to pay taxes and comply with the system.
Cologne school of tax psychology was the first to establish the term tax morale in the 1960s1. However, the term garnered minimal interest among tax academics. At the beginning of the 1990s, tax morale drew widespread interest and has since become a fundamental problem in the scholarly investigation of tax compliance. As a result, tax morale was defined as the sum of all non-monetary reasons and causes for tax reporting that lie beyond the predicted value maximization. This intrinsic incentive to pay income tax is said to be predominantly the outcome of interactions between official and unofficial entities.
After the establishment of tax morale theory, a lot of researches were set. Among them was the Allingham and Sandmo early model. This model characterized tax avoidance of people as a gamble. Given a certain inspection likelihood and a punishment equal to the avoided tax, a question of what percentage of the earnings do cautious citizens declare once they have purely self-interested priorities were set. Further research has revealed that the overall likelihood of investigations and the punishment rate are incapable of explaining why individuals in some nations contribute such a significant amount of income taxes based on the presumption of self-interested motives.
Later, it became vital to recognize that individual qualities have a role in determining a person’s tax morale and behavior. Researchers have found that some people, called “honest taxpayers,” do not try to circumvent taxes as they are just “predisposed not to evade”. The other extremity is represented by “tax evaders,” who mainly have poor tax morale and act rationally when weighing the advantages of avoiding taxes rather than the rewards of cooperating. Moreover, some people may prefer evading taxes and perceive it as a competition in which they are battling with the government.
However, one crucial assumption in the tax morale theory is its duality that is defined by recognizing personal interests and creating suitable policy reactions. While tax morale is usually referred to as one idea, it would be more appropriately defined as a collection of fundamental incentives for tax compliance. Recognizing personal interests and creating suitable policy reactions require locating the routes via which tax morale works. As a result, five widely characterized possible pathways for tax morale have been identified, emphasizing that these systems are not necessarily exclusive and are likely to overlap and interact with one another. The determination of these key pathways played a significant role in later studies.
The first mechanism is a motivational factor of a state’s taxpayer. The motivational factor may be considered an extra component in the utility function that increases the amount of taxes that the person chooses to pay. The second mechanism is congruence, wherein an additional utility term for paying income tax is dependent on the person’s connection to the government in a specific form. Another mechanism is emotions, peer influences, and social factors, wherein the added utility term for paying taxes is influenced by the attitudes or activities of other people. Long-run cultural variables are amongst the processes, as they may influence tax compliance. The last mechanism is inaccurate data and deviations from value maximization.
Therefore, the history of tax morale theory is relatively new, starting its existence in the early 60s in the Cologne school of tax psychology. While not gaining interest and acknowledgment of economic scholars immediately, the theory became widely spread later. As a result of many studies, tax morale theory expanded, now constituting a collection of fundamental incentives for tax compliance and specific characteristics of tax compliance behavior.
Tax Morality
According to many studies of tax morality, the term “tax morale” refers to the willingness of the individual to comply with the tax system. Tax morality is bound to measure the taxpayer’s perceptions and attitudes towards tax compliance and tax avoidance. Therefore, tax morality focuses on the behavior of a person and their relationship with the community and authorities. The main objectives include the research of integrity, influences, and other characteristics of community members.
Taxes create, symbolize, and sustain community connections between specific entities. These relationships bind a single citizen to the government while also uniting the citizens who comply with the taxation process. The tax system does not create an equal tax ratio and, in this regard, no congruent ties among taxpayer and internal revenue services. Instead, it involves obligations that assist the broader public through asymmetrical reciprocity. Furthermore, the concept of “vertical and horizontal fiscal justice” assists in organizing the entire tax-paying population as a society based on the cooperative concept4. Thus, there are specific relationships and interactions which define tax morality.
Such types of interactions are interconnected and ethically valued. These values present themselves in concepts such as faith, accountability, and integrity, which are constantly and inevitably noted in tax-related discussions. While related, the systems of interactions are nevertheless viewed as independent, resulting in a split in the latter ethical concepts. For example, a lack of tax integrity is considered a crime against the government and robbery of compatriots. The government, over all else, represents an anonymous partner of the taxpayer, consisting of a hidden world of reinforced “administrative and executive institutions at the local, state, and federal levels”4. Meanwhile, the taxpayer is a group of affected individuals emerging in the shape of a cooperative matter.
Many areas indicate the level of tax morality in various societies. For example, tax morale is often stronger in countries with tax-heavy economies. Although there is considerable variance across nations, the natural trend is that countries with the highest tax-to-GDP ratios have better tax morale. This factor might be indicative of a vicious loop between successful state functioning, improved tax compliance, along with tax morale; alternatively, it could be indicative of a “fiscal contract between taxpayers and the state,” with citizens eager to pay tax in exchange for efficient social services5. This dynamic will be investigated using regional-level data in further paragraphs.
Moreover, age, educational background, gender, and faith in the state tend to impact tax morale, according to updated information from public opinion polls. When the current worldwide research is compared to the prior scientific assessment from eight years ago, it is clear that many of the same characteristics seem to impact tax morale. People who are “older, more educated, or religious,” as well as women for that matter, have notably higher levels of tax morale at the world scale. Those who have a higher level of faith in the administration also have a higher level of tax morale. These findings are replicated in national analyses, particularly in Latin America, with minor outliers in Africa.
While females have better tax morale than males on a worldwide scale, they have lower tax morale in Africa. The grounds for this are unknown, and the results underscore the need for additional study on gender and taxes, particularly how “unpaid care is addressed in the tax system” and tax discrepancies between female- and male-dominated industries. Nowadays, such a study is impeded by a shortage of related information. Additional thorough statistics, which is presently only accessible for Africa, suggest that the relative value of the tax system is a significant factor of tax morale. According to research findings, the acknowledged validity of the tax authorities is the most important factor of tax morale in Africa.
Statistics from Africa show a favorable association between tax morale and government service provision, but statistics from Latin America offer a less inherent connection. Africa demonstrated higher tax morale, which was connected to satisfaction with governmental services, thereby suggesting the presence of the economic relationship. In Latin America, where faith in the administration was crucial, this association was less clear, although better satisfaction with healthcare was connected with lower tax morale. Additionally, this contradicts prior results, implying that the economical compact may be poorer than previously thought, particularly in fields such as healthcare, where the government’s role is shifting, and people make significant monetary contributions.
Hence, tax morality is the willingness of the individual to comply with the tax system. Meanwhile, tax morality also covers the behavioral patterns of taxpayers and the connections of an individual to the community and the authorities. Additionally, there are many factors that contribute to the tax morality and are therefore its determinants. As a result, the factors later influence the economies and behaviors of taxpayers of various counties.
Factors Affecting the Morality
As it has been mentioned before, tax morality involves the ability and determination to pay one’s dues, such as taxes. Tax morality is one of the integral parts of the economy in both developing and developed countries. Therefore, while being a determinant of economic health, there are many factors that determine tax morality and drive individuals to comply with the established tax system of the state.
The first factor that determines the level of tax morality among citizens is the country’s gross domestic product. Governments with higher tax rates as a proportion of GDP seem to have better tax morale. Therefore, there is a significant relationship between a government’s tax morale and its tax-to-GDP ratio. This statement might certainly illustrate the regional differences, as OECD nations and Latin America have larger tax-to-GDP ratios than other areas. Thus, such a ratio determines the tax compliance of citizens and is a significant factor of morality.
There are many assumptions of why the GDP ratio has a heavy influence on various countries. One explanation is that the association suggests a vicious loop of public service delivery, optional taxpayer compliance, and economic sustainability difficulties, all of which are difficult to manage across many emerging economies. Further correlations, including the influence of casualness on tax morale, might be of importance, but resource restrictions prevent this sort of exercise for the time being.
Another factor of tax morality is highly tied to structural and socioeconomic issues. Tax morale is affected by more faith in government, age, and educational background. The worldwide study result emphasizes the importance of socioeconomic conditions in explaining people’s tax morale. Therefore, people who have a better educational experience tend to have a positive attitude toward tax payments. Another result is that women outperform males in terms of tax morale.
A further condition is intertwined with elderly individuals who are less prone than youths to rationalize tax evasion. Moreover, individuals of the nation in which they live have more excellent tax morale than non-citizens. The last socioeconomic condition is “a faith or religious identity” since religious people are more likely to pay their taxes. Therefore, such socioeconomic factors dictate the tax compliance of people.
According to structural factors, organizational factors and effectiveness are also likely to have a substantial influence on tax morale. People who think that they live in a political system with meritocracy have much higher tax morale. Individuals who trust their political system are more likely to pay their taxes than those who do not. Moreover, those who believe that economic equalization is vital, such as taxing the wealthy to fund benefits for the poor, have greater tax morale. The last structural condition involves people who believe that democracy is the ideal type of government for their nation, which makes them more likely to believe that tax evasion is unacceptable. Thus, the perceptions of equality and inequality, actions of administrations, and the idea of meritocracy in the state contribute to tax compliance behavior.
As a result, the given factors have one common element: government effectiveness and sensitivity to communities’ demands generate tax morale. Trust in the system is determined by how efficient the authority is at keeping its commitments. In contrast, recognized meritocracy depends on administrations assisting in creating a culture in which hard effort leads to prosperity and possibilities are open to everybody.
Studies Related to Tax Morale
There are many studies covering the essence and significance of tax morale. In many types of research, tax morality refers to the moral responsibility to pay taxes or the conviction that tax payment is a way of contributing to the community. Previous studies indicate that tax morality plays a significant role in understanding taxpayer actions and that a great level of tax compliance may be described by tax morale. Other researchers have also discovered that an improvement in tax morale has a considerable favorable influence on individuals’ tax filing and cooperation.
In many studies, tax evasions and tax morale are connected and therefore researched together. Tax morale was examined in Lago-Penas’s study as well as Frey and Weck-Hannemann’s research. In order to investigate the influence of changing trends separately, Simonovits used tax morale as a starting point. They established a value function that accounted for the benefit obtained from the act of disclosing as well as the utility based on the personal expenditure. Earnings redistribution and the delivery of public services are both financed by taxation. The ideal report strikes a compromise between increased consumption as a result of the reduced report and increased ethical value as a result of the greater report. The work concludes that increased tax morale leads to more redistribution of income and gross taxation, hence funding a higher level of government spending.
Traxler developed a more detailed version in which the ethical value from disclosing is directly linked to the number of violators. Traxler also used Allingham and Sandmo’s inspecting and sanctioning module. Allingham and Sandmo’s theory states that taxpayers’ compliance depends on the probability of detection. The presence of equilibrium has now become a complicated matter, and the probability of it cannot be eliminated.
Another segment of the research, such as Bloomquist or Szabó’s, adapted the cognitive method to taxation difficulties. Such approaches are commonly referred to as agent-based models. By far, the most prominent notable example is Hokamp and Pickhardt’s. This example employs four kinds of actors: rational agents, which are the equivalents of conventional egoistic utility maximizers; moralists, who pay their debts; erratics, who make poor decisions, enabling earnings overreporting; and emulators, who mimic the behavior patterns of their neighbors and friends within the community. Antunes, Frey and Torgler, and Prinz offer comparable variants. Therefore, these models all have one common trait; they don’t make any assumptions about people’s norms.
Hence, there are many studies that cover tax morality and explain the importance of researching and integrating tax compliance behavior and taxpayers’ relationships. While many studies concentrate on various divisions of tax morality, all of them have mutual characteristics, such as improvements of tax morale, indicators of tax morality, and reasons for tax evasion. The given examples of studies indicate models of taxpayers and the connection between exemption and tax evasion.
Comparison of Tax Morality between Countries
Tax collections provide authorities with the finances they require to employ in growth, alleviate inequality, provide social programs, and construct the infrastructure necessary for long-term prosperity. Many emerging countries, meanwhile, encounter difficulties in raising their taxes from internal sources. These difficulties include a tiny tax foundation, a vast unorganized economy, inadequate management and administrative ability, low rates of income per capita, internal spending and investment, and perhaps tax evasion by the rich.
Despite the fact that there is a significant association between a government’s degree of development and its tax collections, there are substantial variations across nations at equivalent phases of development. Some nations’ citizens are content to pay their dues, for example, all Ghanaians, while others are not, for example, the majority of Serbians.Therefore, citizens in nations with low tax morale regard tax evasion as reasonable. They may watch everyone else in their community evading taxes and thus believe it is fair and ethical for them to do so as well. The more people who escape examination in a community, the lesser the risk of investigation.
Lago-Peas and Lago-Peas provide a brief summary of the elements discovered in earlier studies as influencing tax morale. They demonstrate that “age, religion, financial stress, and agreement with government decisions” enhance tax morale, but academic achievement and self-employment status decrease tax morale. Fewer shadow economies are also related to higher tax morale. Torgler discovers that Central and Eastern European nations have greater tax morale than former Soviet Union countries involved. Cummings concludes, based on field research in Botswana and South Africa, as well as a study of African countries, that higher tax morale leads to greater tax compliance.
Data Collected from three different national public polls by OECD – Afrobarometer, AsiaBarometer, and Latinobarómetro – reflects national patterns. Countries in Africa have the tax agency that has the authority to compel citizens to obey the tax system at any time. This demonstrates, at least theoretically, reasonably strong support for tax enforcement throughout Africa, with more than two-thirds of participants in the comprehensive study agreeing with the claim, albeit there is substantial variance among nations. The Latinobarometro poses the same question, allowing for a comparative evaluation of the topic of tax morale.
Tax morale is typically high throughout Latin America and the Caribbean, with major variations between nations. The AsiaBarometer study expressly associates public spending with taxation. Respondents in the research were questioned whether they wanted more or less public spending, with the understanding that increased spending may necessitate a tax raise. Citizens generally prefer more public spending, yet there is substantial diversity between nations in Asia, like in other areas. The national statistics reveal a number of additional characteristics that impact tax morale, including satisfaction with public services and budgets, faith in government, and views of wrongdoing.
Satisfaction with government spending and operations may be used to measure how successfully countries transform revenues into expenditures. Tax morale is influenced by contentment with areas such as healthcare, education, water, and sanitation. Education may thus yield a twofold profit, both in terms of inherent advantages and happiness with its supply. The unsatisfied customer engagement is the converse of this, in which more unhappiness with government services is connected with lower tax morale. Efforts to raise people’s knowledge of the connection between tax income and government spending may aid in improving tax morale. Therefore, a lot of results depend on the actions of the government.
If individuals regard their state to be reliable, they are more inclined to view tax burdens favorably. Trust in the system, for example, is connected with a need for more expenditure in Asia. A greater level of commitment and tax morale is connected with a state that is perceived to be making excellent use of tax income, amongst other variables. As previously said, this demonstrates how highlighting the advantages of taxes and spending may boost compliance.
Hence, tax morale in counties varies, with some countries having high levels of tax compliance and other countries dealing with tax evasions and dishonesty. According to the literature, the desire and motivation to pay income tax is the direct result of an interaction between two entities, official and unofficial. This interaction, therefore, predicts tax morale in different countries. Thus, the results of the research show that individuals are more eager to pay taxes if personal interests are involved, and there is a stable policy regarding this topic.
Additionally, some parameters that influence the integrity of citizens and their desire to cooperate with the tax system were identified. The literature used in this paper shows that countries that provide people with proper healthcare, education, and public services tend to have higher tax morale. Meanwhile, countries with lower GDP, education, and healthcare system have a lower level of tax compliance among citizens. Thus, the overall level of contentment of communities plays an integral part in tax morale establishment. As a result, a lack of strong policy and a feeling of impunity play a crucial role in tax morale.
History of Taxation
The tax system has always been a fundamental problem in economics since it is one of all governments’ core activities and a fundamental prerequisite for everything else they undertake. Taxation shifted resources from the individual to the government sector, facilitating the provision of public services such as the legal system, protection, schooling, infrastructure, and healthcare. Premodern nations taxed a broad and diversified array of items, but the underlying tax system was typically relatively straightforward. Individuals, property or its production, and the transportation of commodities were all taxed by the government.
The history of taxation dates back to ancient times. Around 3000 B.C., Egypt recorded the earliest instance of regulated taxes. Taxation later evolved when Greek civilization invaded most of Europe, Northern Africa, and the Mideast in the decades preceding the Common Era. As a result, during earlier eras and throughout medieval European history, new taxes were levied on inheritances, property, and consumer goods.
The two most notable characteristics of the premodern tax system are its vague relationship to the economy and its severe regressive nature. The fundamental differences in premodern tax arrangements were related to the growth of urban areas, trade, and capitalism. Governments that lacked these elements depended on direct taxation of people or property, while governments in more industrially prosperous regions had a more diverse tax system and focused more on indirect taxation.
Britain was at the heart of this process, having experimented with the income tax in 1798–1802 to fund the Napoleonic wars before establishing it officially in 1842. The income tax spread fast across Europe, and by 1920, it was implemented in practically all established European countries. Though the income tax did not significantly raise tax collections in the early stages since it was mainly restricted to the wealthy, the establishment of the income tax is the milestone in the establishment of progressive taxation.
Therefore, the creation of the income tax was the most significant milestone in the history of the premodern tax system, contributing to closely connecting taxes to the economy and drastically improving progressivity. While the taxation system was usually used during war times, with centuries, it became an integral part of the economic structure of the government. However, the problem of taxation started with intentional tax avoidance, which, in return, caused the establishment of specific laws.
Taxes in the Modern World
Capital taxes emerged in the 20th century as part of the Western push toward more progressive taxation, with the USA at the forefront of this evolution. When globalization lowered the cost of capital mobility, some expected a death spiral in capital taxes, but this has not occurred. The explanation for this is that a number of variables, including political institutions and policy decisions, reduce the impact of globalization on capital taxation. The developed nations (Northern Europe and the USA) are the best at tax administration, nations considerably behind (Southern Europe and Eastern Europe) lag behind, and African countries are the worst performers.
Several modern less-developed countries have largely privatized their tax administration since it has grown so problematic. While this is not a reversion to premodern taxation, it is a departure from traditional administrative management. African countries present this taxation trend with the exact precision. African republics’ centralized institutions inherited from former colonies developed into corrupt administrations filled with trade ties that generated little money.
Tax evasion is a huge issue even in the greatest contemporary governmental institutions. Additionally, many corporations exercise tax avoidance to keep the revenue. For instance, the tax gap—the percentage of overall tax liabilities that are not paid—for the United States income tax is around 14%, and more than half of corporate revenue goes unreported. Between 1965 and 2010, tax evasion was perhaps the most severe financial fraud in the USA, accounting for 5% of GDP on average, with the total for all offenses being 7%.
Introduction of Taxes in the UAE
The Emirates opted to create a tax system in their government due to falling oil prices worldwide, reducing the country’s earnings. In order to regulate these earnings, the state decided to introduce a taxation system. The UAE announced in 2011 that it would begin the process of establishing a VAT with a suggested 5% rate that would be introduced in 2014 or 2015.
Personal income tax is not levied in the United Arab Emirates. However, the country does levy corporate taxes on oil firms and international banks. In September 2016, the UAE established Federal Tax Authority by Federal Decree-Law No. 13 of 2018. The FTA is responsible for the collection, and enforcement of tax laws and penalties, in addition to the allocation of tax revenues and the execution of the Tax Procedures.
Subsequently, on August 2017 the UAE issued Federal Decree-Law No. (7) of 2017 on Excise Tax. Later Federal Decree-Law No. (8) of 2017 on Value Added Tax was issued. While the Excise tax is imposed on some commodities that are often dangerous to human health and the environment, the majority of products and services are subject to Value Added Tax. It is a tax levied on customers and collected by the corporation on behalf of the government. VAT is levied on the final consumer of any products or services.
The Emirates’ and the state’s rapid growth plans and VAT implementation comprise a crucial policy change aimed at assisting GCC countries in achieving medium to long-term social and economic policy objectives. The implementation of VAT has aided the United Arab Emirate’s attempts to accelerate its development. The VAT system is a vital strategy that can aid in the transformation of the GCC government and the attainment of long-term economic and social development.
Analysis of Surveys Responses and Interviews on the Effects of Tax Morality and Tax Compliance
One of the daunting things about being an adult is financing the government through paying taxes. An increase in taxes means an increase in pricing for services and commodities, which bores holes in people’s pockets, especially in developing countries. In 2018, the United Arab Emirates introduced a Value Added Tax of 5% on every product as the country could not sustain itself through revenue from oil only. This decision was the best foot forward in maintaining the country’s economy and finance for projects that would attract foreign investors, strengthen tourism, and develop more state-of-the-art infrastructure. With added commodities’ pricing due to the Value Added Tax (VAT) and giving more money to the government, it is hard for some people to keep paying taxes. The levy is burdensome, especially on businesses who are supposed to increase prices in their goods and services and still compete with various markets, including international markets, in selling their products. Therefore, there is a tendency among individuals and businesses not to comply with tax payments. Based on various surveys from civilians on their tax payment experience and interviews from tax collectors and auditors, paying taxes is not a blissful experience. However, it is a civic duty that every citizen needs to undertake. This paper analyzes reports from the surveys and interviews on tax morality and the workability of the tax laws on the economy.
Tax morality is a moral practice that determines if individuals pay taxes according to the appropriate tax rate and rules. Many tax systems depend on taxpayers’ desire to comply with rules and regulations to pay their tax dues; hence tax morality is critical. One of the essential aspects of tax morality is to ensure a fair collection of taxes. The taxes help increase the county’s gross domestic product (GDP), especially in the United Arab Emirates, where oil prices reduced significantly due to increased competition, especially from the OPEC countries. Nonetheless, there should be an equal levy of taxes on items depending on their market price. For instance, the tax levy on a 30-dirham dress cannot be the same as a 25 million dirham gas chromatography machine. Therefore, tax morality ensures fairness and enforcement of tax payments.
An increased VAT registration proves the workability of the tax laws over the years since 2018. According to the government report, there was a sharp increase in VAT registrations between 2018 and 2019 due to application of new tax laws. This increase resulted from the introduction of the laws, which critically affected some businesses at first. In addition, from 2019 through to 2021, the curve has gradually risen as people and businesses adjust to the tax laws. Nonetheless, the government has developed more projects such as increased infrastructure within the three years compared to previous years due to increased revenue. Therefore, the figures on the VAT registration prove that people believe in the tax system and the tax laws bore fruits.
The various surveys show different responses referring to their notions about the tax laws, how it impacts their lives, and the workability of the laws. 79.66% of the respondents noted that the taxes were reasonable in the survey. Comparing UAE to other countries, the country has a low VAT of 5%, which the majority of the citizens can pay comfortably. Most of the respondents, 86.44%, also acknowledged that the taxing systems were fair enough for them. 61.02% of them note that it was easy to understand the tax laws. Federal Decree-Law No. (8) of 2017 is the tax law that describes the tax range, rates, tax liability, and provision of goods and services. Besides the doubt on how tax money is used, 89.83% note that the tax money is used in enriching citizens’ lives. From the survey, 96.61% acknowledge that it is their civic duty to pay taxes and prove one’s loyalty to the country. 33.90% of the respondents note that some tax exemptions harm UAE residents, resulting in inequality, with the rest negating the fact and believing that these exemptions hurt nobody.
Additionally, 47.46% of the respondents believed that the tax system needed to be reformed, while the rest acknowledged that the system is exemplary the way it is. 61.02% of the respondents believe that when other taxpayers fail to pay taxes, it has a negative ripple effect on the regular taxpayers. According to Miller, the country has a set budget to run operations which requires collective input from many people to reduce the price paid per person. Therefore, the more people pay their taxes, and the more affordable the tax rates are because of the increased tax collected. Nonetheless, 76.27% of the respondents acknowledge that United Arab Emirates residents uphold high tax morality. The survey to this point was a yes or no questionnaire.
In the next leg of questions, the survey consists of multiple choices. More than 56% acknowledge that evading tax payment is unethical as a reason for evading tax, while 35.42% feel that the tax is too high for someone to take that money off their income. 52.08% chose that the government takes legal action upon those who do not comply with the tax laws. The more significant percentage of 85.42%, chose that instead of legal action on non-taxpayers, the government should school them on the need for paying tax. Out of 48 respondents, 25 of them, being the most significant percentage, believe that paying a fine would be the best enforcement incentive compared to small fines, arrest, audit, or prosecution. Other than that, the survey response includes educating people on the importance of taxes as the most voted option for a community-based initiative for tax compliance and teaching people how the government spends the money. This move clarifies any doubts about the government or anyone helping themselves with the tax money. More than half of the group voted for lower tax rates, while others considered exempting small businesses in a particular industry struggling from paying taxes would help. This survey helped in quantifying people’s views on tax compliance.
Nonetheless, the study incorporates interviews from people concerned with tax enforcement. The respondent emphasizes the need to pay taxes, as it is one’s civic duty, and there is no need to defy paying taxes. Zafarullah writes on the importance of taxes in the United Arab Emirates. It helps the government see through various development projects and how the country cannot rely on oil money alone. Therefore, The respondent sees no reason people should evade paying taxes because it shows a lack of civic duty and morality. To him, businesses and individual taxpayers have the same tax evasion habits. However, tax evasion has improved over the years, with enforcement the best way to ensure tax compliance. The respondent’s interview highlights that tax evasion is a problem that people create.
Moreover, a senior tax auditor acknowledges that tax evasion is an evident problem because the government does not stipulate how it uses tax money. People barely see how they benefit from paying taxes. Bardhan also raises this concern, noting how corruption is at 5%, and politicians seem to benefit from taxes by considering their interests. Nonetheless, The respondent notes that the tax evasion issue is due to the taxpayer’s distrust of government operations. To The respondent, tax evasion is illegal, thus the reason for complying with tax payment. As many people, especially individuals, are finding better ways of evading tax, The respondent believes that the government should use incentives like rewards and enforcement like penalties to make people pay taxes. The respondent’s thoughts question the government’s use of taxes in development, a widespread belief with many individuals that causes them not to pay taxes.
Additionally, in another interview with a tax enforcer, the problem of tax evasion is tied to economical struggles where people barely pay taxes due to lack of employment and the need to save money. Tax evasion is not morally right to the respondent as businesses are more elusive than individuals. However, the tax evasion problem improves with people learning more about taxes and understanding the need to pay taxes. According to Zafarullah, the government introduces paying taxes through primary education and progresses to show how to pay them. The heavy penalties levied are also a constant reminder of the need of people to file their taxes, such as it is in the UAE where the penalty may levy an individual with a 300% tax penalty for evading payment for a month past the deadline. However, with rising unemployment rates in the country, there is a need for the system to be changed so that people can easily comply with the tax payment.
Tax morality and paying taxes diligently significantly impact the economy. One common issue highlighted among the three interviews is that morality is not a basis for tax payment; instead, the system needs to develop just ways of ensuring tax compliance. As a recommendation from the surveys and interviews, educating the masses on the importance of tax compliance would help in increasing tax payment. In addition, non-taxpayers should pay a significant fine to ensure tax morality. As many people voted for lower tax rates, the UAE has significantly low tax rates already and is still sustaining itself well. Therefore, a decrease in taxes would cost the country some major development projects and decrease economic output.
Additionally, the charging of taxes to citizens should also fairly apply to non-UAE residents in the United Arab Emirates. In most cases, international charges vary with the citizens, were international residents tend to pay more for items and services. However, most aliens are trying to make a living, and imposing heavy tax duties would hurt them financially. It is understandable if heavy tax laws are imposed on tourists rather than non-UAE residents. Lastly, the government should be held accountable for using the taxes, which would enable the citizens to trust the entity with their hard-earned money. In conclusion, the survey response and interviews provide a holistic view of the UAE taxing system and its impact on the country’s economic growth.
Final Chapter
The current paper discusses value-added tax (VAT), the significance of tax morality for people and country, and their effect on tax law compliance in the UAE. The current section summarizes the main findings on the importance of tax morality, the impact of VAT on the economy, tax compliance for 2018-2021, and provides recommendations for improving tax morality. Despite all the government’s efforts and adopted laws to collect VAT for the country’s development, the commitment can be insufficient if people have low tax morality, which indicates the need for its improvement.
Summary
Taxes are an essential aspect of the state’s functioning, but their collection can cause population resistance. The tax systems have a long history, which even reaches the times of ancient Egypt. Despite such a lengthy development background, modern tax systems still develop and face serious problems. As oil revenue decreased, the UAE adopted the Federal Decree-Law no. (8) to establish the VAT several years ago. The introduction of VAT increases the cost of products and services for consumers. On the one hand, more taxes will allow the state to finance health care, defense, and other areas to improve the population’s well-being. On the other hand, higher prices reduce residents’ savings and can cause their discontent. Tax morality is a concept that describes the commitment of residents to pay all taxes imposed by the state. The state and residents’ well-being largely depends on this morality.
The concept of tax morality is relatively new, but it is increasingly attracting attention. Tax morality embraces not only the level of desire to pay taxes but also the attitude of residents to the tax system and their relationship with the government. Taxes are the key sources of income for the state to finance the development of the state subsequently. The lower the desire to pay taxes, that is, low tax morality, the fewer resources for the country’s development and the support of residents. For this reason, the population’s morality is essential for state functioning and prosperity. At the same time, taxes must not be a heavy burden for the people since residents will not afford the products necessary for their well-being with too high taxes.
The decline in oil profits has led the UAE government to seek additional sources to support the state’s pace of development. The mentioned law imposes a VAT with a 5% rate for a significant number of end products and services. Paying taxes when making a purchase is inevitable, and residents cannot avoid this tax. Still, it can affect tax morality regarding attitude to the system and the state and interfere with compliance with future laws. In case of the wrong approach to introducing taxes, confidence in the government will decrease. Moreover, a significant burden falls on business operators as tax collection agents, which can damage their reputation and business. This situation underlines the importance of improving tax morality for the UAE population.
After the adoption of Federal Decree-Law no. (8), there have been changes in the UAE economy. The number of VAT registrations increased over time. Moreover, the introduction of VAT caused public concern about the subsequent taxes and the negative impact on personal savings. Nevertheless, the government has received new opportunities for investing in the country’s development and attracting additional sponsors. By 2021, revenues amounted to about $26 billion, which allowed a high sovereign credit rating and strengthened the field curve for dirham. Improved tax morality is necessary to maintain high tax revenues.
Observation
Key observations needed to provide recommendations in this study include aspects affecting tax morality level in residents and its current assessment in the UAE population. Many studies have researched the issue of influence factors for morality, and therefore one can distinguish several separate components. First of all, respect for laws, including the payment of taxes, is formed by the personal qualities of residents. Upbringing, culture, level of education, and even religiosity can influence their opinions. A strong effect on the attitude to taxes is exerted by the person’s environment – relatives, friends, and other people who are part of the circle of interaction. In addition to individual-level factors, one can also distinguish broader trends.
An example of a more significant influence is the GDP level – the higher it is, the better the commitment to paying taxes. Socioeconomic conditions are also an essential factor since residents, who feel the support and care of their state, trust the government more. Moreover, a high level of education is also significant since the educated population understands the importance of taxes. There is also a higher morality among residents than non-residents and in the younger generation in socioeconomic terms. Such structural factors as trust in the government and its bodies, faith in the system existing in the country, and equality are also critical. Studying factors that contribute to tax morality allows allocating directions to provide recommendations to improve it.
An important aspect is understanding the current level of tax morality among UAE residents. Surveys demonstrate that most residents consider the tax with a 5% rate moderate and recognize that the tax system is fair. Moreover, almost all UAE residents recognize that paying taxes is an essential civic duty and that money is used to improve the population’s lives. residents also note the need to inform the public about taxes and propose some concessions for small businesses, to which the tax payment can cause a loss. The study also includes interviews with several people interested in tax policy. All of them note that tax evasion is unethical and consider it a socioeconomic problem caused by unemployment. They also highlight the importance of education in tax issues. Thus, one can conclude that the inhabitants of the UAE have a high tax morality, and efforts should be aimed at supporting it.
Recommendation
Based on the findings presented earlier in the current paper, several recommendations can be distinguished to establish and maintain a high tax morality among the UAE population.
- Consciousness. Supporting the high level of awareness of the population, in particular tax awareness, is key to improved tax morality. Understanding the need for tax payments to maintain the population’s well-being will support compliance. Survey participants and tax policy stakeholders noted the need to disseminate knowledge about taxes. Moreover, the importance of education in the tax issue is confirmed by various studies researching the effects of tax literacy. Therefore, the UAE government needs to provide important information about tax decisions and their impact in an understandable way for its residents. Highlighting the advantages of taxes and spending may boost compliance among residents.
- Trust in the government. This recommendation covers several issues in the activities of the government. Its efforts should be aimed at the population’s well-being, and decisions should be carefully considered before adoption. Providing the people with the best services, developed infrastructure, health care, and supporting the economy contributes to high tax morality. Moreover, the government must maintain transparency and accountability in its actions. These measures are necessary for people to understand and trust their government’s actions. The sense of security provided by the state, support for equality, and faith in the system, push the population to the necessary compliance.
- Enforcement. Many theorists and researchers are confident that the possibility of detention and punishment for tax evasion is an effective measure to support compliance. However, the government should be cautious with this measure, as it may worsen relations with the population. Moreover, some studies prove that residents’ understanding of their duties contributes more to the adherence to laws. Thus, a legal framework for organizing taxes is needed, but the measure should not be leading in ensuring tax morality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tax morality significantly impacts the residents’ compliance with tax laws. With the clear and transparent work of the government, tax revenues are directed to the well-being of the state and its population. Tax morality depends on education, social environment, level of education, understanding of tax issues, trust in the state, and similar factors. In 2018, the UAE adopted a law imposing a tax of 5% on final services and goods, and it is necessary to maintain high tax morality among the population. At the moment, most residents support tax policy, believing that it is pretty fair. It is essential to inform residents about taxes and maintain their trust in the government through honest and transparent work to keep a high level of morality.
Bibliography
Alasfour, F., Samy, M., & Bampton, R. (2016). The determinants of tax morale and tax compliance: Evidence from Jordan. In Advances in taxation. Emerald Group Publishing Limited. Web.
Alkhodre, A., Jan, S., Khusro, S., Ali, T., Alsaawy, Y., & Yasar, M. (2019). A blockchain-based value added tax (VAT) system: Saudi Arabia as a use-case. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 10(9), 708-716. Web.
Allingham, M. G., & Sandmo, A. (1972). Income tax evasion: A theoretical analysis. Journal of Public Economics, 1, 323-338. Web.
Almansoori, H. K., ‘Tax Evasion and its Effect on Criminal Liability under UAE Tax Law’, Journal of Sharia and Law, vol. 2019, no. 79, 2019. Web.
Approved VAT Registrations (Federal Tax Authority 2022) Web.
Bardhan, P. Corruption and development: a review of issues. Political Corruption. 2017.
Batrancea, L., Nichita, A., Olsen, J., Kogler, C., Kirchler, E., Hoelzl, E.,… & Zukauskas, S. (2019). Trust and power as determinants of tax compliance across 44 nations. Journal of Economic Psychology, 74, 4-66. Web.
Bazart, C., Bonein, A., Hokamp, S., & Seibold, G. (2016). Behavioural economics and tax evasion: calibrating an agent-based econophysics model with experimental tax compliance data. Journal of Tax Administration, 2(1), 126-144. Web.
Beraja, P. (2016). Analysis of the Middle East fashion and luxury market: success of UAE through the prism of economic development and consumer behavior transformation. Web.
‘Consumer Reactions to VAT Implementation in UAE’, 4Signt Global, 2018, Web.
D’Amore-McKim School of Business. (2020). A brief History of Taxation. Northeastern University. Web.
Di Gioacchino, D. and Fichera, D., ‘Tax Evasion and Tax Morale: A Social Network Analysis’, European Journal of Political Economy, vol. 65, 2020, p.1-14. Web.
Enachescu, J., Olsen, J., Kogler, C., Zeelenberg, M., Breugelmans, S. M., & Kirchler, E. (2019). The role of emotions in tax compliance behavior: A mixed-methods approach. Journal of Economic Psychology, 74, 1-16. Web.
Federal Tax Authority. (2016). The establishment of the federal tax authority. Web.
Federal Tax Authority. Federal Decree-Law No. (8) Of 2017 on Value Added Tax. 2017. Web.
Guenther, D. A., Wilson, R. J., & Wu, K. (2019). Tax uncertainty and incremental tax avoidance. The Accounting Review, 94(2), 229-247. Web.
Hakelberg, L., & Seelkopf, L. (2021). Handbook on the Politics of Taxation. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Hoffman, P. T. (2017). Public economics and history: A review of fiscal regimes and the political economy of premodern states. Journal of Economic Literature, 55(4), 1556-1569. Web.
Horodnic, I.A., ‘Tax Morale and Institutional Theory: A Systematic Review’, International Journal of Sociology and Social Policy, vol. 38, no. 9/10, 2018, pp. 868-886, Web.
Kasim, M. A., Mohd Hanafi, S. R., and Mohd Suki, N., ‘What Shapes Muslim Business Operators’ Attitudes Towards Value-Added Tax? Evidence from the United Arab Emirates. Journal of Islamic Marketing, 2020. Web.
Kemme, D. M., Parikh, B., & Steigner, T. (2020). Tax morale and international tax evasion. Journal of World Business, 55(3), 1-12. Web.
Khaerunnisa, I., Wiratno, A., & Luthan, E. (2016). The effect of tax morality, tax culture, and good governance to taxpayers compliance. The Accounting Journal of Binaniaga, 1(1), 59-68. Web.
Kiser, E., & Karceski, S. M. (2017). Political economy of taxation. Annual Review of Political Science, 20, 75-92. Web.
Miller, A. H. (2019, February). Data modeling and visualization of tax strategies employed by overseas American individuals and firms. In International Conference on Emerging Internetworking, Data & Web Technologies (pp. 309-321). Springer, Cham. Web.
Mogielnicki, R., ‘Value-added tax in Gulf Arab states: Balancing domestic, regional, and international interests’, 2019. Web.
mof.gov (2018). UAE law. Web.
Nichita, A., et al., ‘We Learn not for School but for Life: Empirical Evidence of the Impact of Tax Literacy on Tax Compliance’, Eastern European Economics, vol. 57, no. 5, 2019, pp. 397-429. Web.
OECD. (2019). Tax Morale What Drives People and Businesses to Pay Tax? OECD.
PALIL M, TAX KNOWLEDGE AND TAX COMPLIANCE DETERMINANTS IN SELF ASSESSMENT SYSTEM IN MALAYSIA (2010)
Pepinsky, T. B., Pierskalla, J. H., & Sacks, A. (2017). Bureaucracy and service delivery. Annual Review of Political Science, 20, 249-268.
Saderuddin, A., & Barghathi, Y. (2018). The laws of the introduction of VAT on the audit profession and economy in the UAE: Auditors’ perspective. Accounting and Management Information Systems, 17(3), 406-439.
Slemrod, J. ‘Tax Compliance and Enforcement’, Journal of Economic Literature, vol. 57, no. 4, 2019, pp. 904-954,
The Official Portal of the UAE Government. (n.d.). Taxation. Web.
Torgler, B., Demir, I. C., Macintyre, A., & Schaffner, M. (2008). Causes and consequences of tax morale: An empirical investigation. Economic Analysis and Policy, 38(2), 313-339. Web.
‘UAE’s VAT Revenues Reach $26bn Since Implementation’, Arab News. Web.
United Arab Emirates Ministry of Finance, ‘Value Added Tax (VAT)’, United Arab Emirates Ministry of Finance, 2018, Web.
Verma, P., Agarwal, S., & Gupta, D. (2019). Uae Hogging in the Limelight of Vat-1st 2018. Global Journal of Enterprise Information System, 11(1), 131-139. Web.
‘Value Added Tax (VAT) Implementation In UAE | MOFUAE’ (Mof.gov.ae, 2020) Web.
Yaghi, A., & Alibeli, M. (2018). Theoretical and empirical analyses of citizens’ willingness to pay: ethical and policy implications for the environment in United Arab Emirates. Journal of Emerging Trends in Economics and Management Sciences, 9(5), 291-303. Web.
Zafarullah, M. (2018). Impact of VAT on UAE economy. Asian Development Policy Review, 6(1), 41-49.
